Geography of Egypt
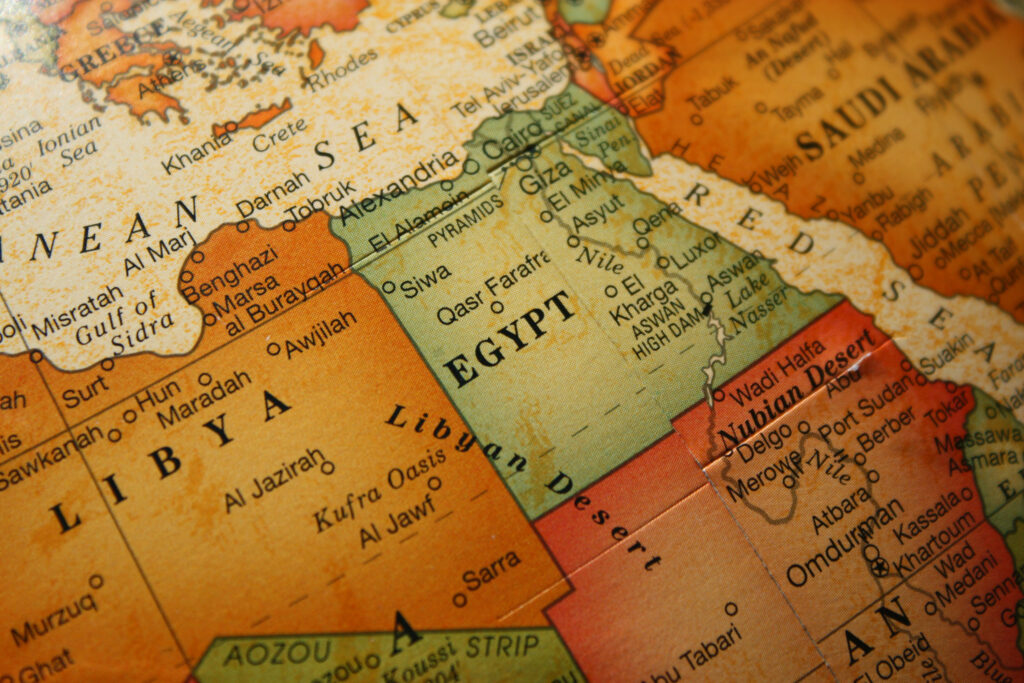
Egypt is a country located in the northeastern corner of Africa, with a small portion of its territory extending into southwestern Asia through the Sinai Peninsula. Here are some key geographical features of Egypt:
Nile River

one of the longest rivers in the world, flows through Egypt from south to north. It has been a crucial resource for the country, providing water for agriculture and supporting the growth of ancient civilizations.
Desert Landscape: Much of Egypt’s land consists of arid desert. The Eastern Desert lies to the east of the Nile, while the Libyan Desert is to the west. The vast Sahara Desert also extends into Egypt.
Sinai Peninsula
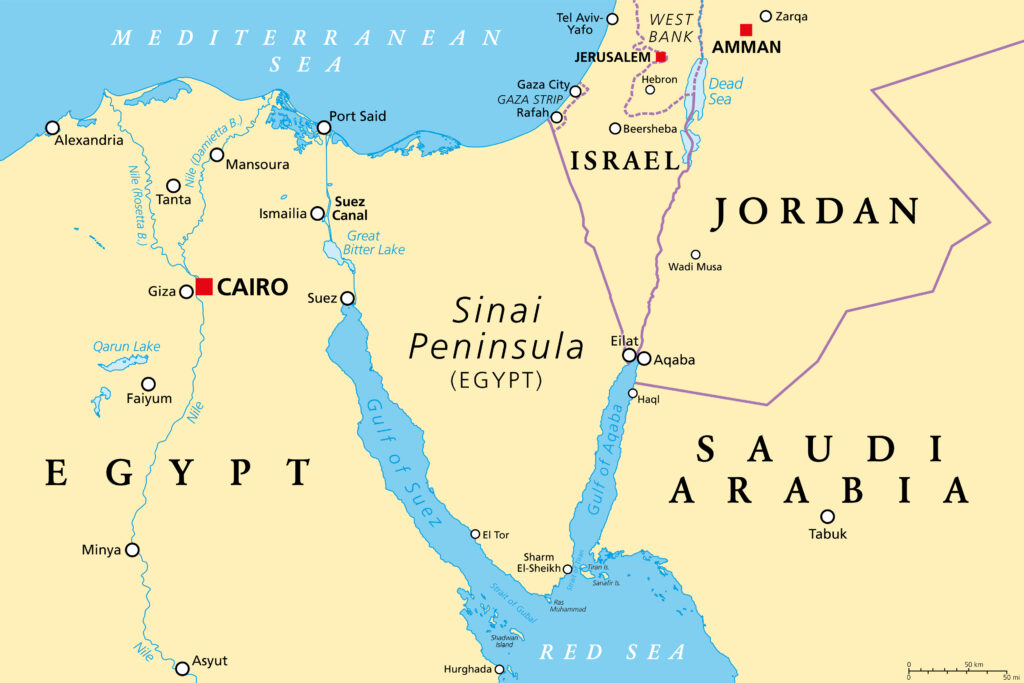
This triangular peninsula is situated between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south. It serves as a land bridge connecting Africa and Asia. The Sinai is characterized by mountainous terrain, including the rugged Sinai Mountains.
Mediterranean Sea
Egypt has a coastline along the Mediterranean Sea to the north. The northern coastal region is known for its fertile Nile Delta, where the Nile River fans out into multiple branches before reaching the sea.

Red Sea
To the east, Egypt has a coastline along the Red Sea. This area is known for its vibrant coral reefs and is a popular destination for tourism and diving.
Places to visit
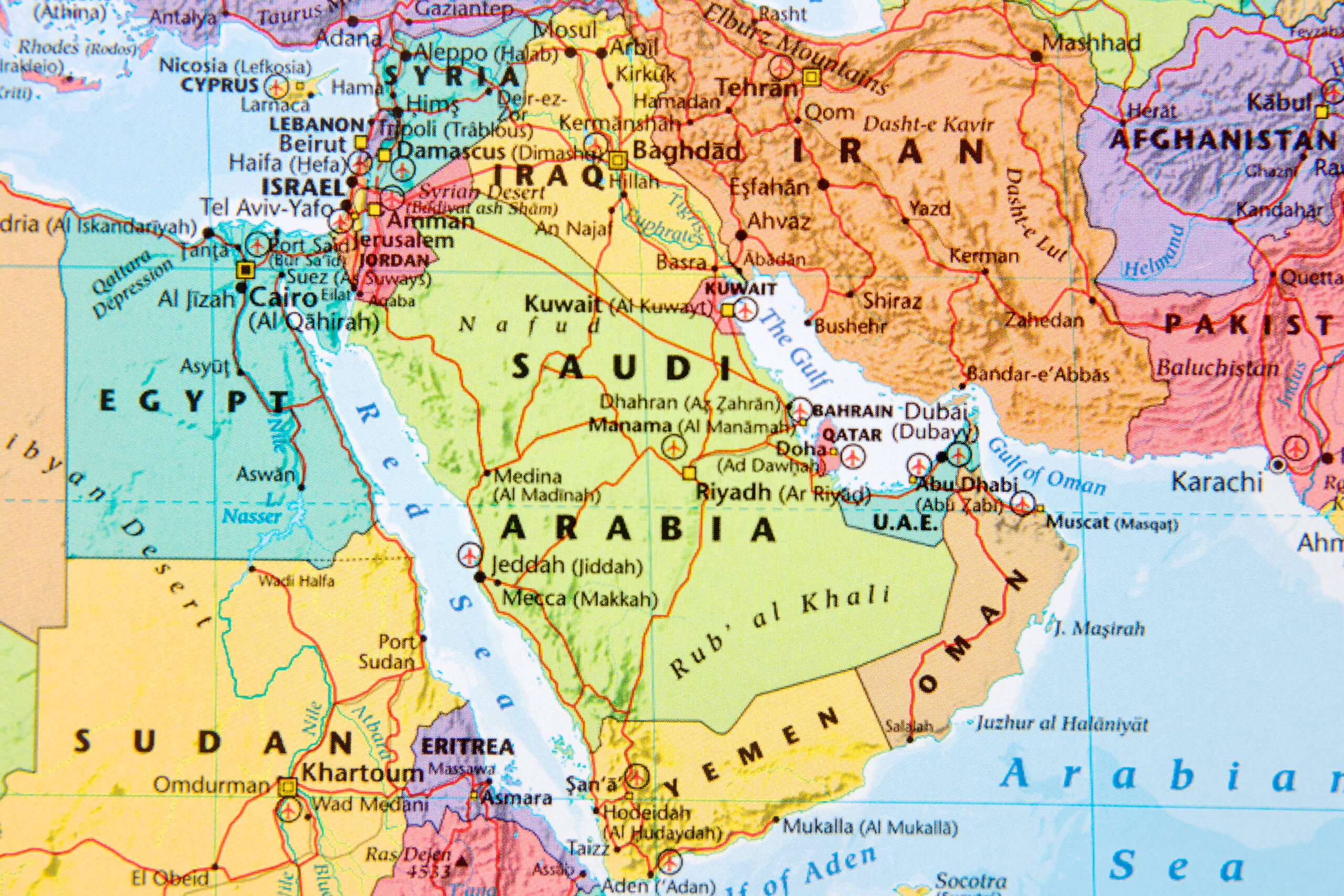
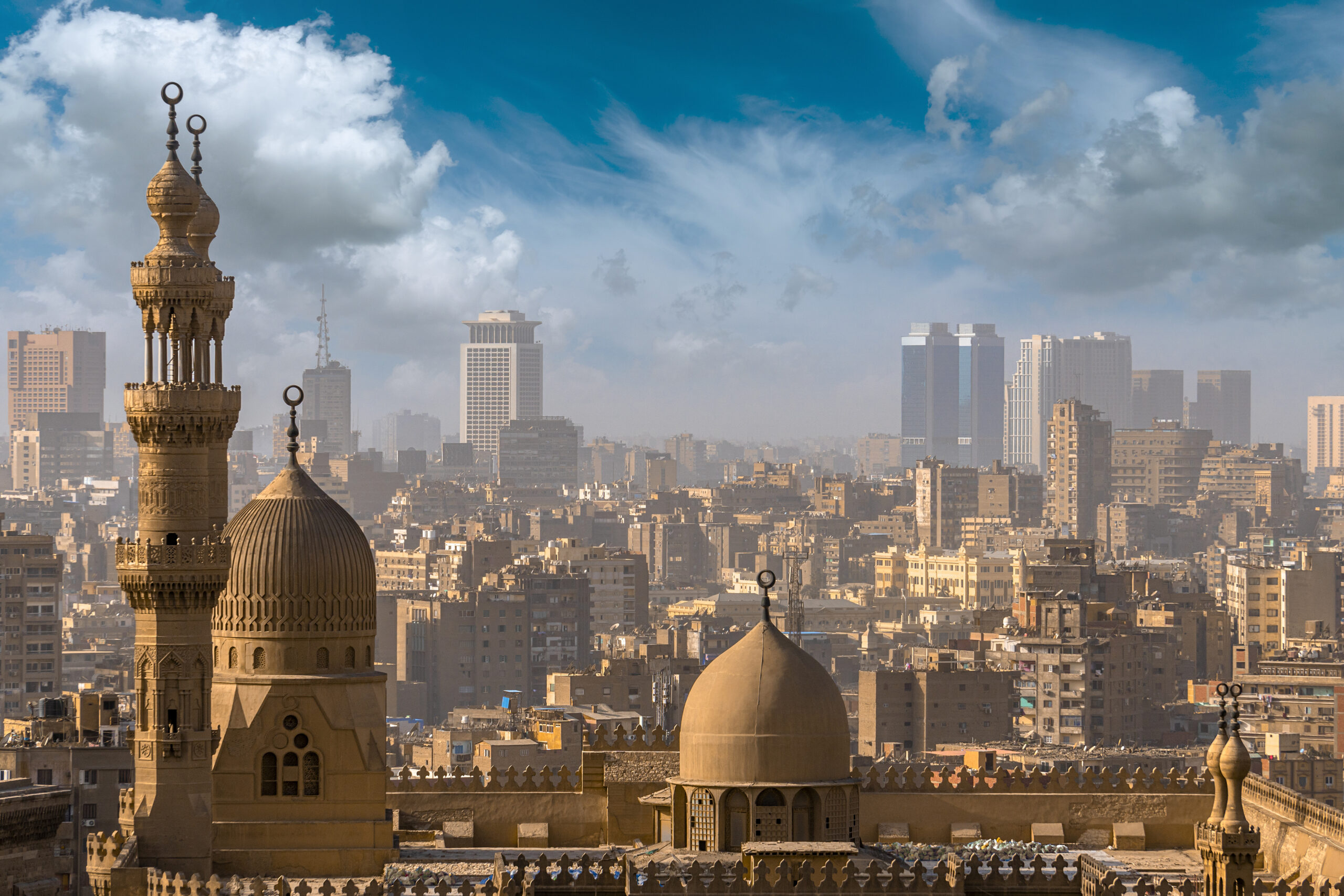
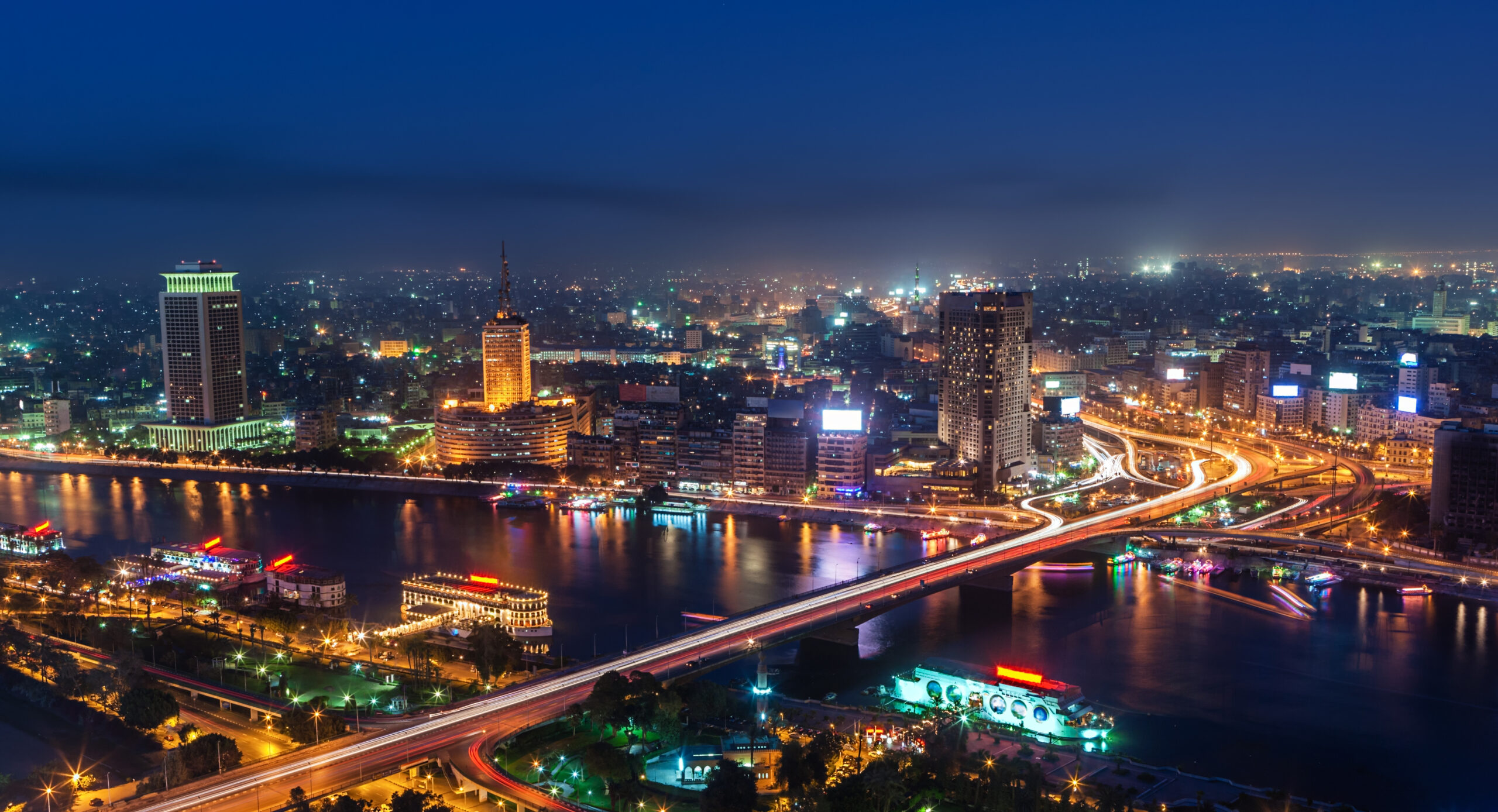
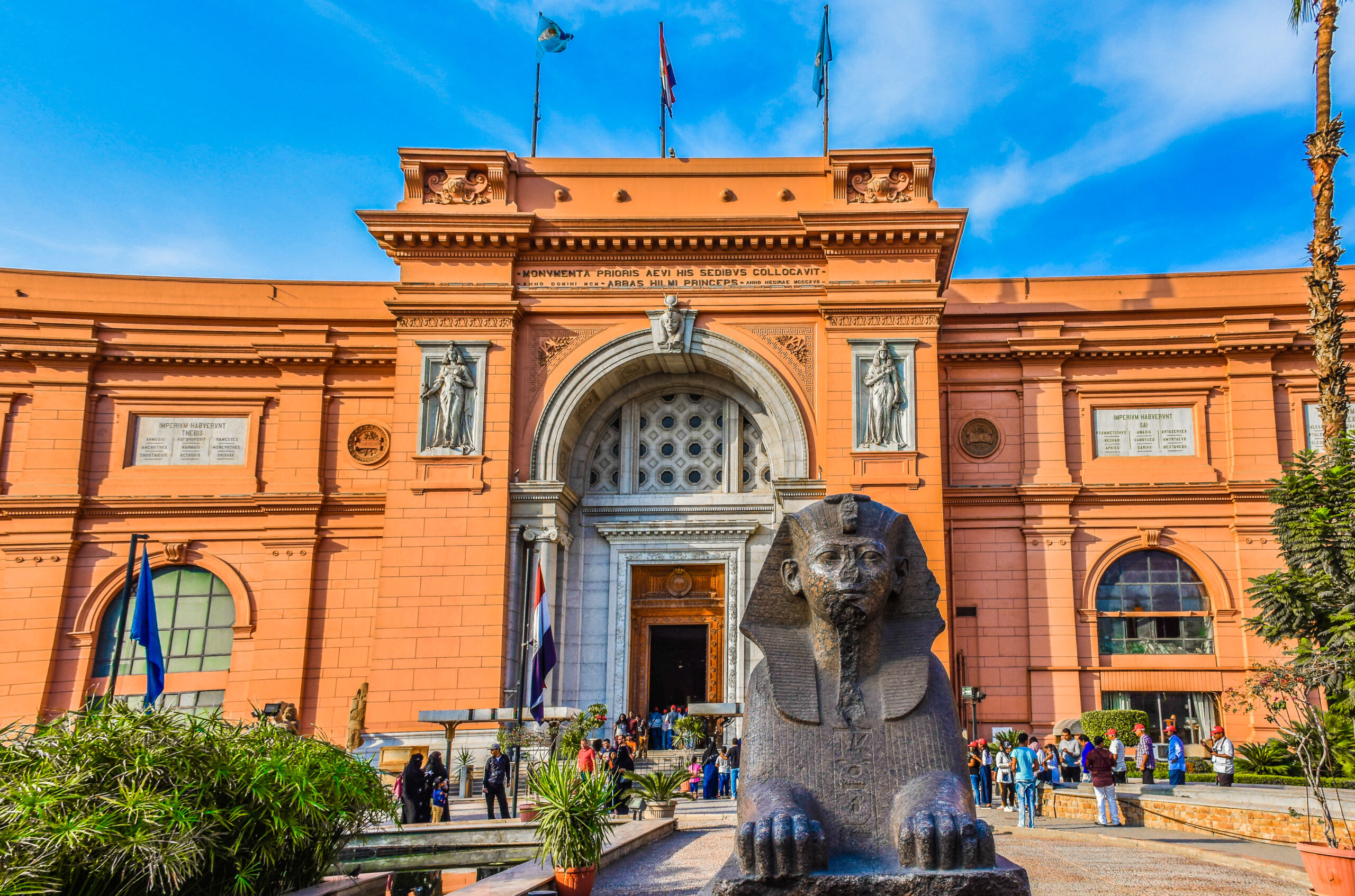
Cairo: The capital city, Cairo, is located along the banks of the Nile River in the north-central part of the country. It is the largest city in Egypt and serves as the political, cultural, and economic hub.
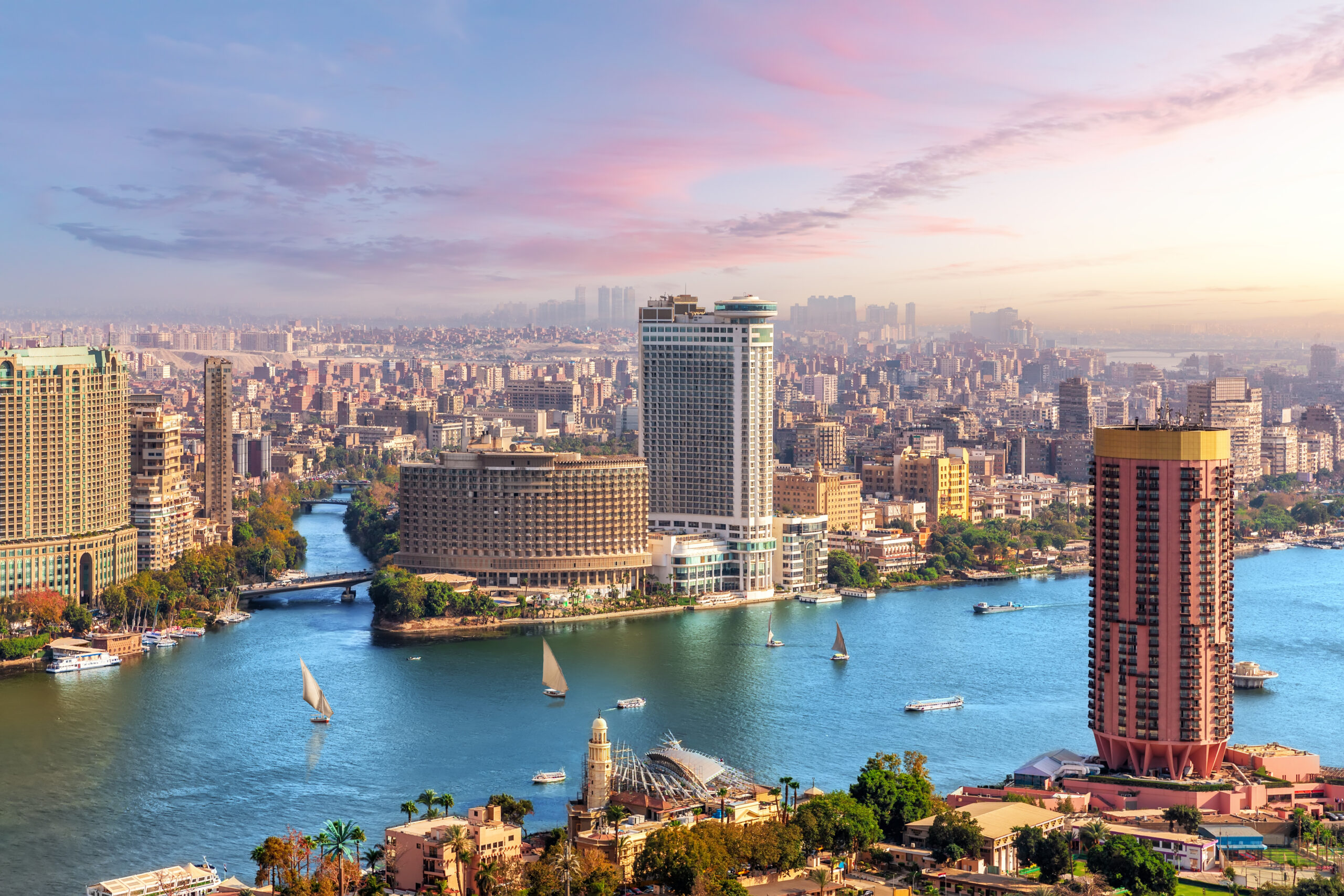
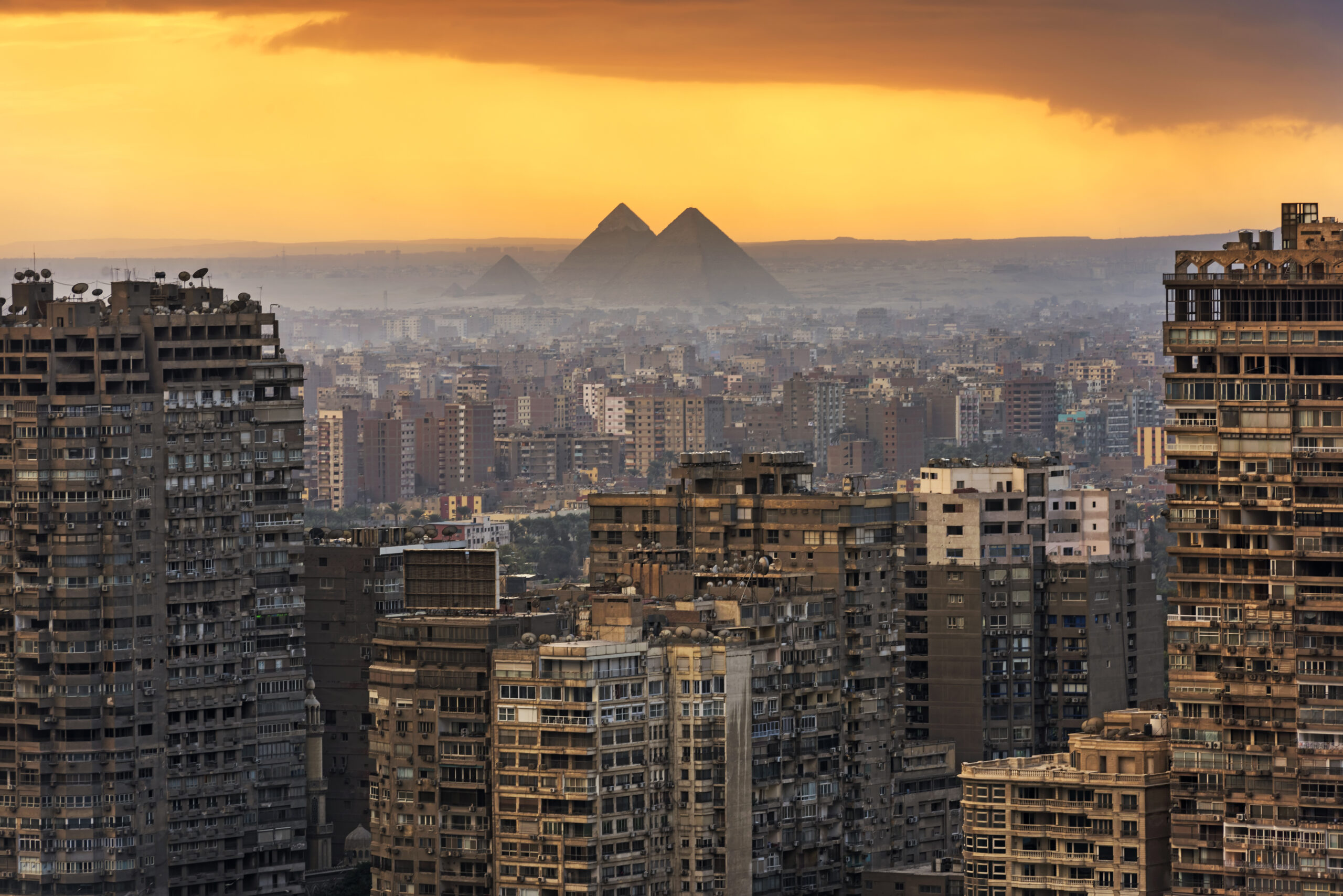
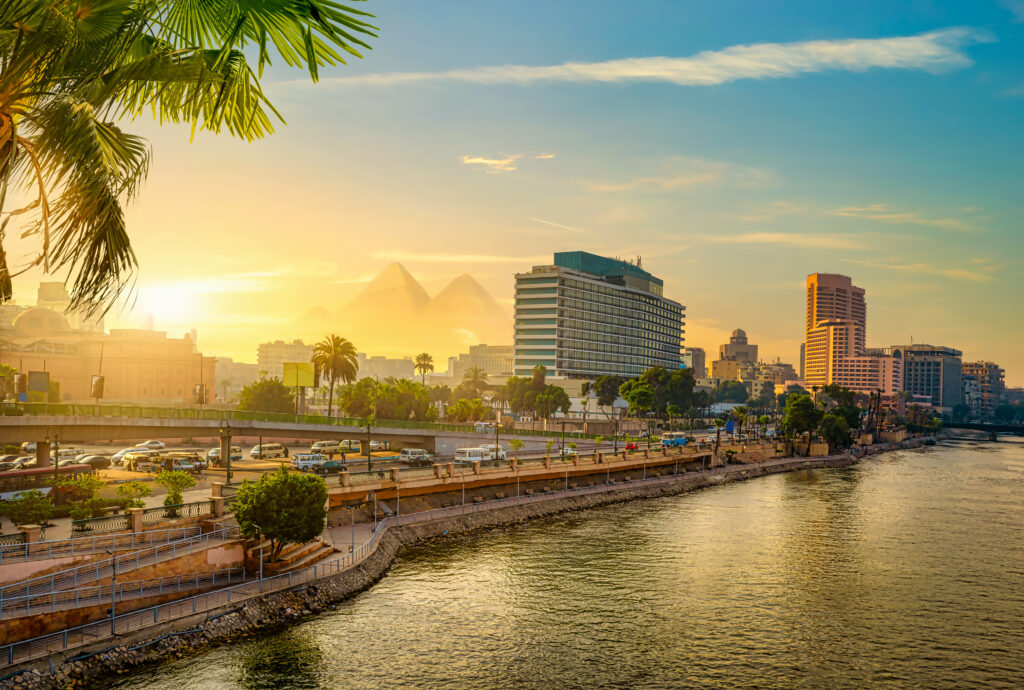







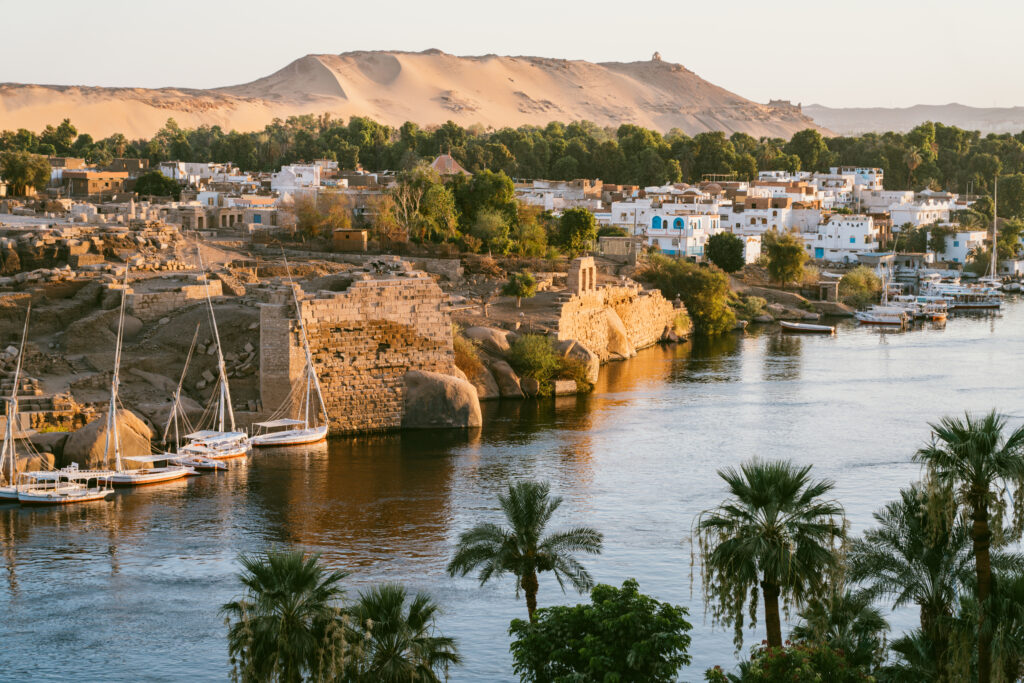
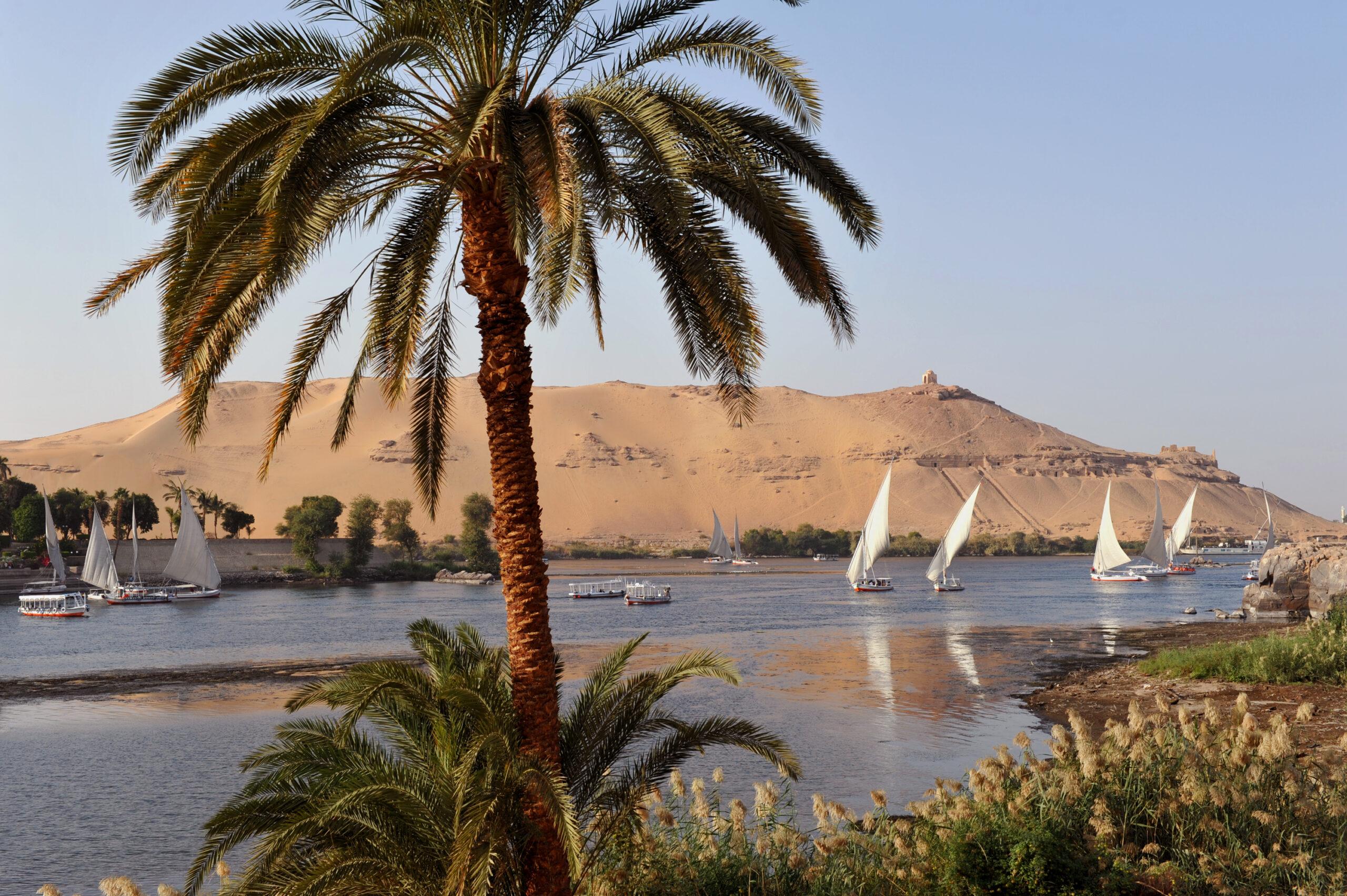
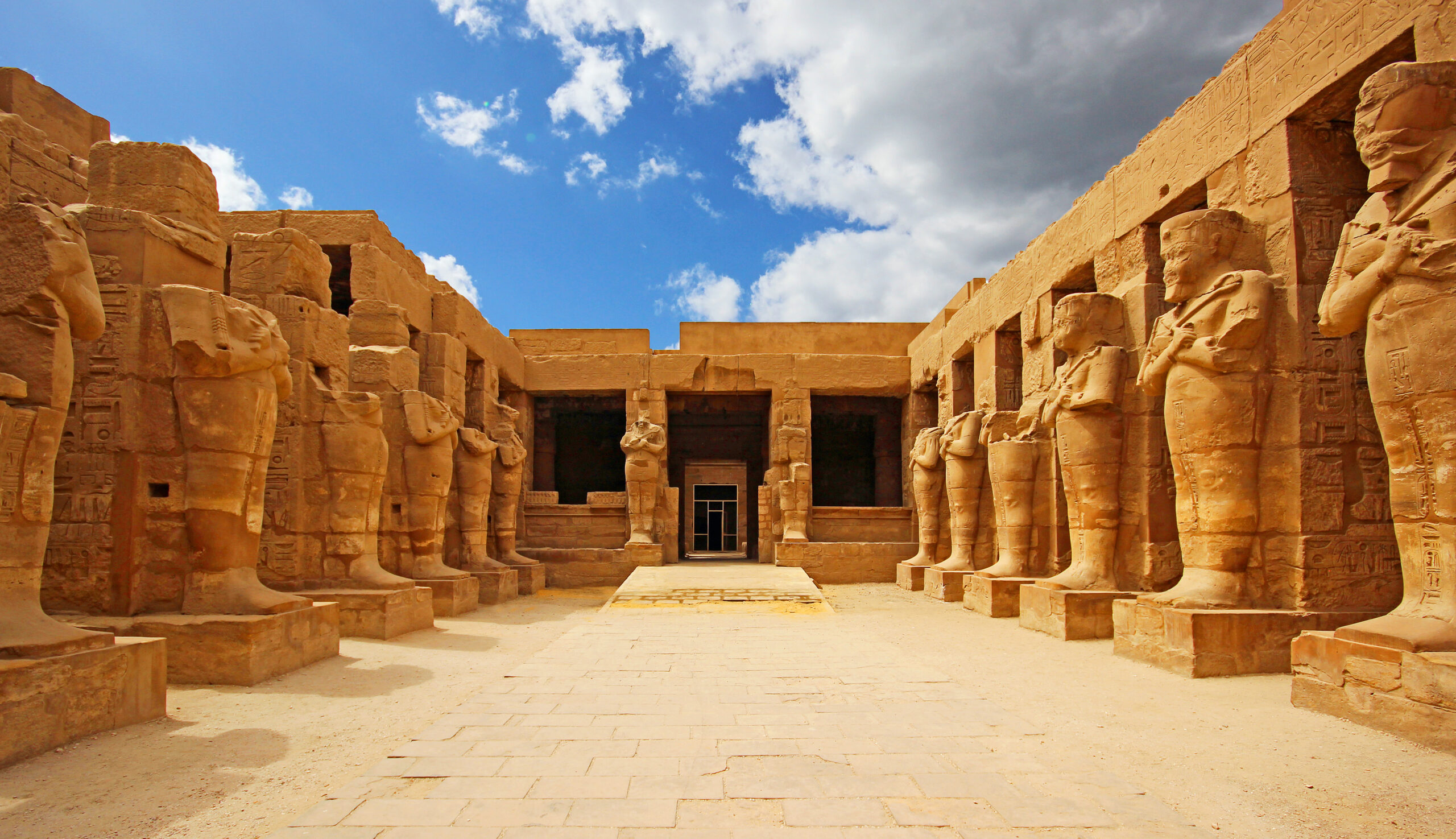
Aswan and Luxor: These cities are located along the Nile and are significant for their historical and archaeological sites. Luxor, in particular, is known for the Valley of the Kings and other ancient monuments.



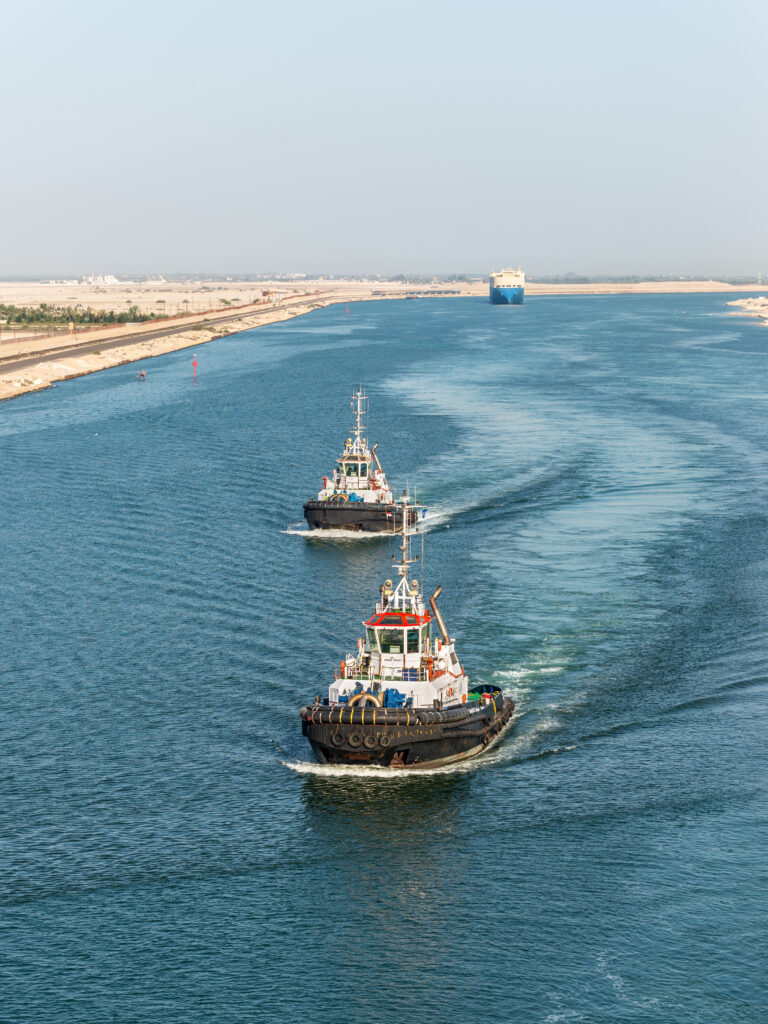
Suez Canal: Connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, the Suez Canal is a vital artificial waterway that facilitates global shipping and trade. It runs through the Isthmus of Suez in northeastern Egypt.

Egypt’s geographical features have played a crucial role in shaping its history, culture, and economy. The fertile land along the Nile has supported agriculture for thousands of years, while the deserts have presented both challenges and opportunities for the people of Egypt.
